1-1. 프로세스, 스레드, 리액티브
1) 프로세스, 스레드
🔰 프로세스
독립된 실행의 단위
과거
- CPU - 프로세스가 독점
- memory - 프로세스가 메모리 공간을 자유롭게 사용
현대
- CPU - OS의 스케줄러에 의해 time slice(정해진 시간)만큼 실행
- memory - OS로 할당받은 메모리 공간 사용
- CODE, DATA, HEAP, STACK(메모리 공간의 영역을 다시 이렇게 나눔)
🔰 Thread 일반
프로그램은 현재 실행되지 않고 하드디스크 등 주기억 장치에 존재, 컴파일이 되면 아래와 같이 파일의 섹션 단위로 영역이 나뉨.
![[유저 영역과 커널 영역]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/1.png) [유저 영역과 커널 영역]
[유저 영역과 커널 영역]
- 유저 영역 : 힙, 스택, 데이터, 코드 영역
- 커널 영역 : 프로그램이 제어할 수 없는 OS영역
![[운영체제에서 제공하는 메모리 공간]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/2.png) [운영체제에서 제공하는 메모리 공간]
[운영체제에서 제공하는 메모리 공간]
- CODE 영역 : CPU가 이해할 수 있는 바이너리(0101010) 명령어들이 있는 영역
- DATA 영역 : 컴파일 시점에 INTEGER, LONG같은 크기가 정해져 있는 전역변수들이 미리 영역을 확보해 놓음
![[C++ 스택 영역 및 변수 저장 과정]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/4.png) [C++ 스택 영역 및 변수 저장 과정]
[C++ 스택 영역 및 변수 저장 과정]
- 프로세스 : 컴퓨터에서 연속적으로
실행되고 있는 컴퓨터 프로그램. 스케줄링의 대상이 되는 작업(task)이라는 용어와 거의 같은 의미로 쓰임. 여러 개의 프로세서를 사용하는 것을 멀티 프로세싱이라고 하며, 같은 시간에 여러 개의 프로그램을 띄우는 시분할 방식을 멀티태스킹이라고 함.
![[프로세스의 구조]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/6.png) [프로세스의 구조]
[프로세스의 구조]
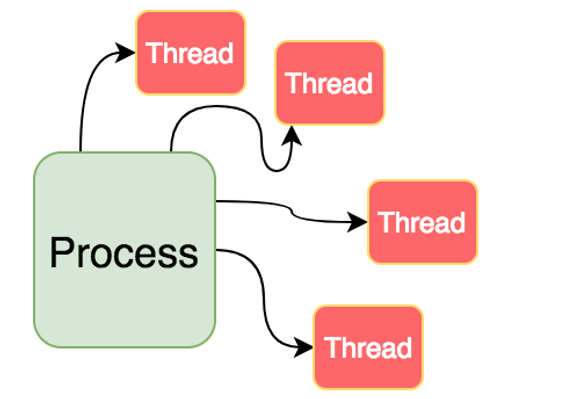
- 스레드 : 어떠한 프로그램 내에서, 특히
프로세스 내에서 실행되는 흐름의 단위를 말함. 일반적으로 한 프로그램은 하나의 스레드를 가지고 있지만, 프로그램 환경에 따라 둘 이상의 스레드를 동시에 실행할 수 있음. 이런 실행 방식을 멀티 스레드라고 함.
![[스레드 구조]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/7.png) [스레드 구조]
[스레드 구조]
- 프로세스 내 스레드는 각각 스택만 따로 있고, Code, Data, Heap 영역은 공유. 같은 프로세스 내 있는 다른 스레드들은 서로 Code, Data, Heap을 공유하지만, 프로세스는 다른 프로세스의 메모리에 직접 접근할 수 없음.
🔰 멀티 스레드와 싱글 스레드
![[멀티 프로세스]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/8.png) [멀티 프로세스]
[멀티 프로세스]
- 싱글 프로세스 : 프로세스가 스레드를 생성하게 되면, 새로운 스레드를 만들 때 테스크 구조체를 만들고 새로운 스레드가 사용할 스택 영역을 만들게 됨.
스택은 스택 트레이스로 함수들이 연결되는 과정이나, 로컬 변수들이 스코프 지정이 일어나는 영역.힙은 스레드들이 서로 공유할 수 있는 영역. - 스레드 생성에는 태스크 구조체와 스택 영역을 확보하고 기타 OS 자원을 확보하는 등의 비용이 필요하지만, 프로세스 하나를 통째로 만드는 것보다 더 가벼움. 멀티프로세스 모델보다 성능이 좋음.
![[멀티 스레드 모델]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/9.png) [멀티 스레드 모델]
[멀티 스레드 모델]
![[싱글스레드 프로세스 모델과 멀티스레드 프로세스 모델]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/10.gif) [싱글스레드 프로세스 모델과 멀티스레드 프로세스 모델]
[싱글스레드 프로세스 모델과 멀티스레드 프로세스 모델]
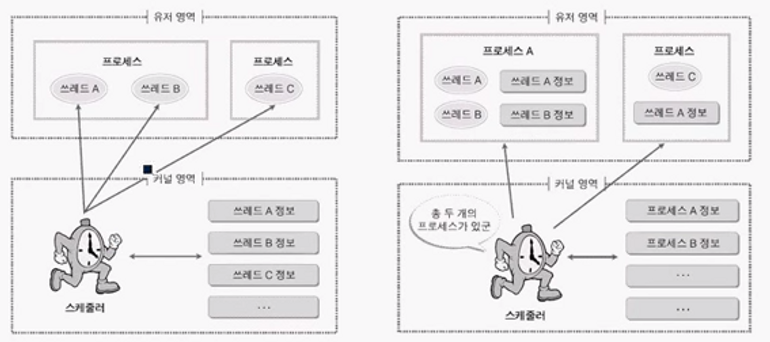
- Context Switch : 스케줄러에 의해 스레드는 time slice만큼 CPU를 사용한 후 작업을 멈추고 CPU를 다음 스레드가 점유하는 것.
🚩 과정
- 저장 : 반납되는 스레드는 마지막 상태를 메모리에 저장
- 복원 : 실행되는 스레드는 메모리에서 저장된 상태를 복구
✔ 콘텍스트 스위치가 많이 일어나면 오버헤드가 발생할 수 있음
🔰 멀티 프로세스 모델과 멀티 스레드 모델
💡 스레드에서는 Heap을 공유할 수 있기 때문에 캐싱 측면에서 스레드 모델 성능이 좋음. 프로세스에서는 서로 메모리 공간을 쉐어할 수 없기 때문에 캐시를 리셋해버림. 그러므로, 하드웨어적으로 멀티 프로세스 모델은 속도 이슈가 있음.
🔰 스레드풀
- 스레드를 미리 만들어 놓고 재사용하는 것.
- 이유 : 비용 감소(스레드 생성 비용 - CPU, Memory)
![[스레드 풀 구조]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/13.png) [스레드 풀 구조]
[스레드 풀 구조]
🔰 스레드 in JVM
![[JVM 구조]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/14.png) [JVM 구조]
[JVM 구조]
- JVM 스레드 비용 : 스레드 생성비용(OS+JVM), 콘텍스트 스위칭, Garbage Collection
- 성능 최적화를 생각한다면 OS thread를 직접 사용할 때보다 더 신경써야 했음.
2) 자바에서는 어떻게 비동기 코드를 만들까?
🔰 비동기가 필요한 상황
- CPU expensive
- CPU 자원을 많이 사용하는 코드들 중 분할가능한 코드는 병렬화, 시간 단축
- I/O blocking
- HDD, network card등 I/O 작업의 완료를 대기한다
- 대기하면서 스레드 자원 낭비
![[동기 비동기]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/15.png) [동기 / 비동기]
[동기 / 비동기]
🔰 JAVA 비동기 API
- java.lang
- class Thread
- void start()
- interface Runnable
- void run()
- class Thread
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// 스레드 동작에 대해서 알아보자
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static Result getAPI() {
System.out.println(111);
return null;
}
//(1)JVM이 할당한 메인 스레드(public static void main 메서드) 실행
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { //(3)새로운 콘텍스트에서 스레드 생성
@Override
public void run() { //(4)새로운 스레드에서 동작
System.out.println("run"); //(5)출력
Result result = getAPI(); //(6)출력
}
});
thread.start(); //(1)스레드 객체 시작
System.out.println("main"); //(2)동작
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
// main (2)
// run (5)
// 111 (6)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// 메인 스레드와 서브 스레드가 독립적으로 진행되며 일어나는 문제점
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static Result getAPI() {
System.out.println(111);
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Map map = new HashMap(); //객체는 jvm heap 영역에 저장됨
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Result result = getAPI();
map.put("API", result);
}
});
thread.start();
System.out.println(map.get("API")); //null
// main 스레드와 서버 스레드(new Thread)는 서로 독립적임
// 서버스레드가 끝나기 전에 main스레드 영역이 끝나버렸기 때문에 null
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
// null
// 111
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// 프로그램이 복잡해지고 notify를 빼먹는다면?
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static Result getAPI() {
System.out.println(111);
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Map map = new HashMap();
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Result result = getAPI();
map.put("API", result);
/*
synchronized (map) {
map.notify();
}
*/
}
});
thread.start();
System.out.println(map.get("API"));
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
🔰 비동기 개발에 사용한 API(1) - Future
- 비동기 작업의 결과를 받아오고 싶을 때.
- Interface Future
- V get() : 값을 가져오기 위해 wait, notify로 했던 작업을 메서드 하나로 추상화.
- boolean isDone()
- Class FutureTask
- interface Callable
- V call()
- Interface Future
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static String getAPI() {
return "111";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() { //Callable 생성
public String call() throws Exception { //스레드에서 동작할 행위들, 즉 콜백 생성
return getAPI();
}
};
ExecutorService es = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//Executors = 스레드 풀 제공, 싱글 스레드만 가지는 executor를 만듬
Future<String> future = es.submit(callable); //callable구현체 submit
String result = future.get(); //서브스레드의 동기화 이슈를 완료해줌
//이 시점에서 서브스레드가 완료될 때까지 블로킹
System.out.println(result); //111
System.out.println(222); //222
es.shutdown();
}
}
// 111
// 222
😨 잘못 사용한 스레드 풀
- newCachedThreadPool
→ 1 client * 7 request ⇒ 1 + 7 (threads)
→ 300 client * 7 request ⇒ 300 + 2100(threads)
🔰 비동기 개발에 사용한 API(2) - CompletableFuture(JDK8)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// 하나의 단일 작업만 처리하는 기존 Future에 대한 문제
// A -> B -> C 와 같은 의존성 있는 태스크를 Future에서 해결하려면?
Future<Result> firstFuture = es.submit(new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Result firstResult = getFirstAPI("HELLO1");
Future secondFuture = es.submit(new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Result secondResult = getSecondAPI(firstResult);
Future thirdFuture = es.submit(new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
return getThirdAPI(secondResult);
}
});
return thirdFuture.get(); //스레드 기다림
}
});
return secondFuture.get(); //스레드 기다림
}
});
//콜백 문제가 생김
//스레드를 계속 기다리고 있기 때문에 자원 낭비
- java.util.concurrent
- class.CompletableFuture
- interface Future
- interface CompetionStage
- interface Future
- class.CompletableFuture
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf = new CompletableFuture<>();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println(111);
cf.complete("hello!");
System.out.println(222);
}
}).start();
String result = cf.get(); //블로킹
//CompletableFure가 가지고 있는 complete()메서드에 값을 assign하게 되면 블로킹 해제, 다음 라인으로 넘어감
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("test");
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
// 111
// 222
// hello!
// test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// 람다식 : 가독성이 좋아짐!
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf = new CompletableFuture<>();
new Thread(() -> cf.complete("hello!")).start();
String result = cf.get();
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("test");
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
// hello!
// test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// 태스크간 순서
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static String getFirstAPI(String msg) {
System.out.println("111");
return "111";
}
public static String getSecondAPI(String param) {
System.out.println("222");
return "222";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
String result = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!") //completedFuture에 "hello"라는 문자를 할당하게 되면 complete하게 됨
.thenApply(msg -> getFirstAPI(msg)) // 111
.thenApply(param -> getSecondAPI(param)) // 222
.get();
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
// 111
// 222
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// thenCombine
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!");
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hi!");
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hallo!");
String msg = cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (x, y) -> x + " " + y)
.thenCombine(cf3, (x, y) -> x + " " + y)
.get();
System.out.println(msg);
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
// hello! hi! hallo!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// 컨텍스트 변경
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
String result = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!!!")
.thenApply(ThreadMain::getFirstAPI)
.thenAcceptAsync(ThreadMain::getSecondAPI)
.get();
//thenApply : 같은 스레드에서 동작
//thenApplyAsync : 새로운 스레드에서 동작
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
🔰 NIO(New IO | Native IO | Non Blocking IO)
❓ Thread Pool 에 FULL이 나는 현상 : 서킷 브레이커 패턴, 서버 증설로 해결하지만, 더 좋은 방법이 없을까? ⇒
Non Blocking
NIO- jdk 1.4 nio
- jdk 1.7 nio2
New IO- Native IO
- Nonblocking IO
packages- java.nio
- java.nio.channels
- java.nio.channels.spo
- java.nio.charset
- java.nio.charset.api
- java.nio.file
- java.nio.file.attribute
- java.nio.file.spi
✔ 네이티브 : 기존 데이터는 JVM의 heap메모리 공간에 카피를 해야 했음. 카피한 것으로 핸들링을 해야 했지만, 네이티브는 원래 네이티브 데이터를 가지고 핸들링할 수 있음. 카피 비용이 줄어들기 때문에 성능적으로 월등함.
![[Non Blocking IO]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/16.png) [Non Blocking IO]
[Non Blocking IO]
💡 (1) client - selector 에 붙는 단위를 channel이라고 함.
(2) client부터 request을 받은 selector는 순차적으로 핸들러에게 줌.
(3) 핸들러는 각각 client의 요청을 동작시키고 response해 줌. (IO작업을 단일 스레드로 처리 가능)
🔰 비동기 개발에 사용한 API(3) - Non Blocking IO
- Servlet 3.0
- AsyncServlet →
*스레드 : 논블로킹하고 별개
- AsyncServlet →
- Servlet 3.1
- Nonblocking IO
- Spring MVC : DeferredResult
2) 리액티브
🔰 Event Programming
- CompetableFuture나 Non blocking IO 방식의 공통점 : 이벤트 방식 처리(이벤트 발생 → 처리)
- 이벤트 발생 : CompletableFuture.complete(“값”);
- 이벤트 처리 : CompletableFuture.thenApply(“콜백”);
💡
이벤트란?
- 프로그램에 의해 감지되고 처리될 수 있는 동작이나 사건
- ex. onclick();
이벤트 프로그래밍이란?
- 절차지향 프로그래밍과 비교되는 프로그래밍 패러다임
- 이벤트가 발생한다는 전체를 깔고 이벤트를 처리하는 코드를 작성
- 이벤트가 올 거라고 예상하고 그에 대응하는 반응을 만드는 코드
![[이벤트 드리븐 패턴]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/17.jpg) [이벤트 드리븐 패턴]
[이벤트 드리븐 패턴]
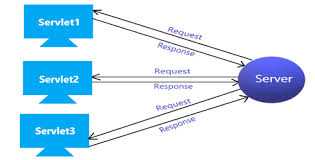 Servlet Request도 이벤트라고 할 수 있음
Servlet Request도 이벤트라고 할 수 있음
💡 소스 → 이벤트를 발생시킴
→ 대기하고 있던 리스너가 이벤트를 받음
→ 핸들러가 이벤트 처리
ex) 브라우저의 request → 이벤트 발생 → 톰캣이 받아서 거기에 맞는 response를 반환
🔰 정리
- 의문 : 이런 이벤트 프로그래밍 관점에서 잘 추상화된 API가 있다면?
- observable, Rxjava, Reactor, sodium, JDK9 Flow, AKKA, etc.
- 웹개발에 활용할 프로임워크 쪽은?
- Spring 5 MVC, AKKA-http, Vert.x Web, Playframework, etc.
-
범위를 좁혀보자
✔ 현장에서 가장 많이 쓰는 자바, 스프링
✔ 리액티브 프로그래밍
- reactive-streams
- Reactor
- Spring 5 MVC
- 성능!
- 백프레셔(backpressure) : 기존에 처리할 수 있는 양만 적절히 처리, 나머지 포기
색인과 출처
1-1. 프로세스, 스레드, 리액티브
- 영상 주소
- 운영체제 제공 메모리
- 프로세스와 스레드
- 서킷 브레이커 패턴
- pass fail
![[운영체제에서 제공하는 메모리 공간]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/3.png)
![[프로세스와 스레드]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abarthdew/trouble-shooting-references/main/images/java/5.png)